












IDC data shows that the global switch market size will reach USD 41.644 billion (approximately CNY 300 billion) in 2024, and is expected to grow to USD 43.867 billion (approximately CNY 316 billion) in 2025. The Chinese market is projected to be CNY 74.9 billion in 2024, and is expected to range between CNY 80.1 billion and 91.5 billion in 2025. In terms of global high-speed switch shipments, there will be 690,000 units in 2024, with TrendForce and Orient Securities predicting 880,000 units in 2025. Data from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology indicate that the localization rate (not market share) is expected to increase to 46.8% in 2025, showing strong momentum for the development of domestic switches.
Driven by multiple demands such as AI, 5G, and data center upgrades, the high-speed optical communication and switch market is experiencing rapid growth. Policies are promoting domestic production and low-carbon development, while emerging scenarios continue to expand boundaries. On the technological front, there is a coordinated evolution toward high speed, intelligence, energy efficiency, and security, with innovations such as CPO, LPO, silicon photonics, and liquid cooling becoming key driving forces.
The competition in computing power for network devices has intensified, and the resulting surge in heat density has brought cooling to the forefront. As the core of the data center, the thermal management of switches has transitioned from behind-the-scenes support to the forefront, becoming one of the decisive factors that determine product competitiveness and market landscape.
The Evolutionary Dilemma of Switch Cooling
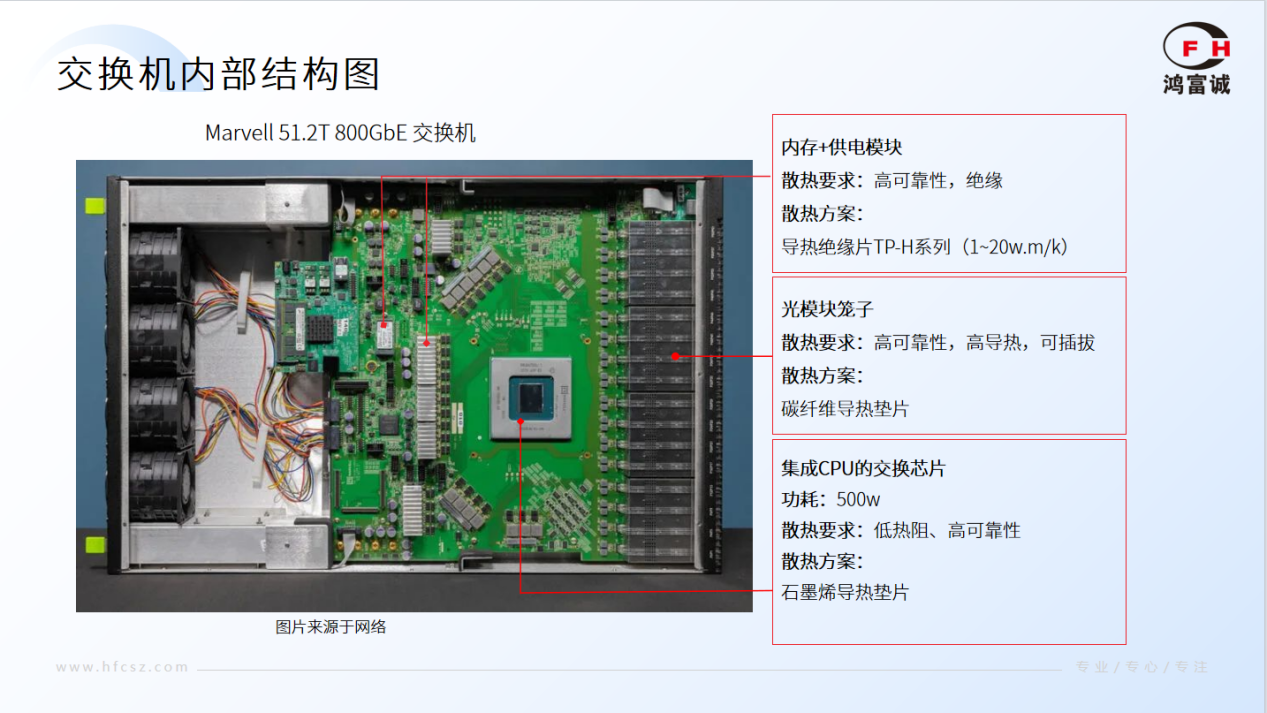
Power Consumption Surge: With the improvement of ASIC chips and CPU processing capabilities in modern switches, the power consumption of high-end switching chips can reach 1500W, with a heat flux density exceeding 100W/cm².Compact Design: Devices are trending toward high-density ports, which limits cooling space. This can lead to heat accumulation, affecting the normal operation and lifespan of the switch.Enclosed Space: Natural convection inside switches is insufficient, relying on forced air cooling or liquid cooling. Core components such as the CPU, switching chips, and optical modules generate significant heat during operation. If heat cannot be dissipated in time, local "hot spots" may form. Continuous high temperatures accelerate component aging, causing performance throttling, data loss, and even hardware thermal failure.Thermal Interface Material Constraints: As devices trend toward high-density ports, cooling space is restricted, leading to heat accumulation and negatively impacting the normal operation and lifespan of the switch.
HFC Graphene Thermal Pads Empower Efficient and Stable Switches
Hfc thermal management solutions focus on providing efficient and reliable thermal management for modern data centers and communication equipment. In addressing the heat dissipation challenges of high-performance switches under heavy loads, we leverage advanced thermal conductive materials and innovative structural designs to significantly enhance equipment cooling efficiency and ensure the long-term stable operation of network devices.

HFC Graphene Thermal Pads
Harnessing Surging Power Consumption to Ensure Stable OperationHongfucheng Graphene Thermal Pads utilize a vertically aligned graphene structure, achieving an ultra-high thermal conductivity of up to 130 W/mK. Their thermal performance is more than 10 times that of conventional thermal interface materials, and the interfacial thermal resistance can be as low as 0.05°C·cm²/W. This enables rapid dissipation of core heat, significantly reduces temperature differences, effectively suppresses localized overheating, ensures stable chip performance, and eliminates the risk of high-temperature throttling and downtime in switches.At the same time, their porous structure offers excellent environmental adaptability, effectively absorbing warping deformation caused by thermal expansion coefficient mismatches, maintaining interface integrity, and keeping thermal channels continuously unobstructed. This makes them especially suitable for the stringent cooling requirements of ultra-high-power ASIC chips in high-end switches, significantly enhancing the long-term reliability of the equipment.
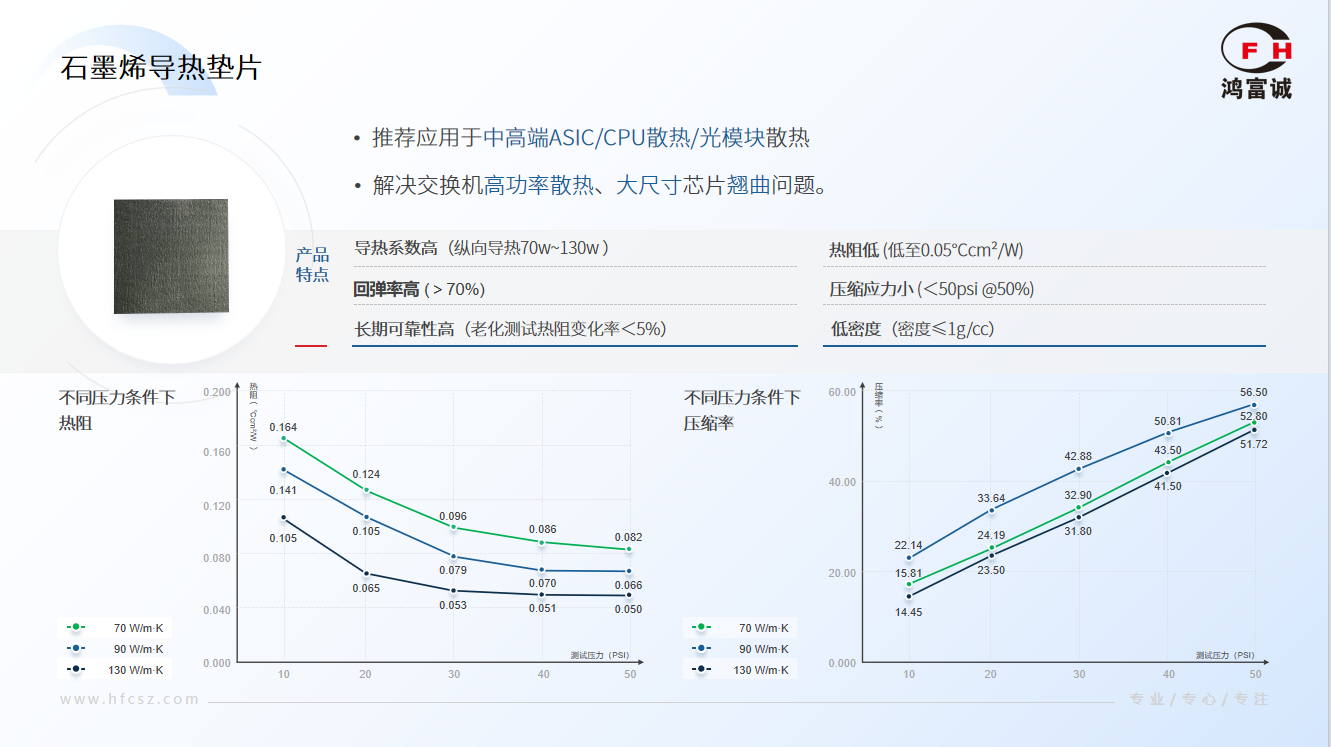
High resilience structure, absorbs deformation, low-stress chip protectionThe porous structure inside the graphene thermal pad provides good compressibility and high resilience. It can adapt to minor deformations, absorb warping displacement, and exert less stress on the chip and PCB. This protects sensitive components (such as BGA solder balls), reduces the risk of solder joint fatigue cracks caused by stress and thermal expansion and contraction, and enhances long-term reliability.

Thousand-Hour Rigorous Validation Reduces Total Maintenance CostsHonFucheng graphene thermal pads undergo rigorous testing (1000 hours of high temperature, temperature cycling, and dual 85 aging tests), resulting in minimal changes in thermal resistance. They are silicone-free or low-volatility, resistant to 'pump-out.' The material maintains stable performance throughout its lifespan, eliminating the need for frequent maintenance. It is suitable for 7x24-hour demanding operational conditions, thereby reducing total maintenance costs.Finally, we can see that HonFucheng's solution not only significantly reduces energy consumption and operational costs but also, with excellent thermal conductivity and reliability, empowers switches to perform at high levels in complex environments, providing critical infrastructure support for AI clusters, cloud computing, and 5G deployment.